
You will require mortgage insurance if you make a mortgage down payment of less than 20%. While there is no set limit on the maximum mortgage amortization period for uninsured mortgages, the maximum for insured mortgages is 25 years. Some mortgage lenders offer 35-year and even 40-year amortization periods. You can check your budget using a mortgage affordability calculator. While this does mean that each payment will be larger, you will be able to pay off your mortgage faster and save potentially thousands in interest costs. It is best to choose as short of an amortization period that you can comfortably afford to pay. However, this will result in more interest being paid overall.

This means that each mortgage payment will be relatively smaller, which can help make payments more affordable for cash-strapped homeowners. Longer amortization periods will spread out the length of your mortgage. The mortgage amortization period that you choose will affect the amount of your mortgage payments and the overall interest paid on your mortgage. The interest of the skipped payment will be added to your mortgage principal, lengthening your amortization period and resulting in more interest paid in the long-run. These skip-a-payment options don’t mean that you’re off the hook for the payment amount. TD, for example, allows you to skip the equivalent of one monthly mortgage payment once per year. Most banks offer some form of mortgage payment deferral to help homeowners during difficult financial periods. Taking advantage of particular prepayment privileges that some mortgage lenders offer, such as RBC’s Double-Up prepayment option or BMO’s 20% annual lump-sum prepayment option, will also reduce your amortization period. This means that you will be paying off your mortgage faster while also saving in interest costs. If you make more frequent mortgage payments, such as by changing from a monthly payment to an accelerated bi-weekly payment, then your amortization period will decrease.
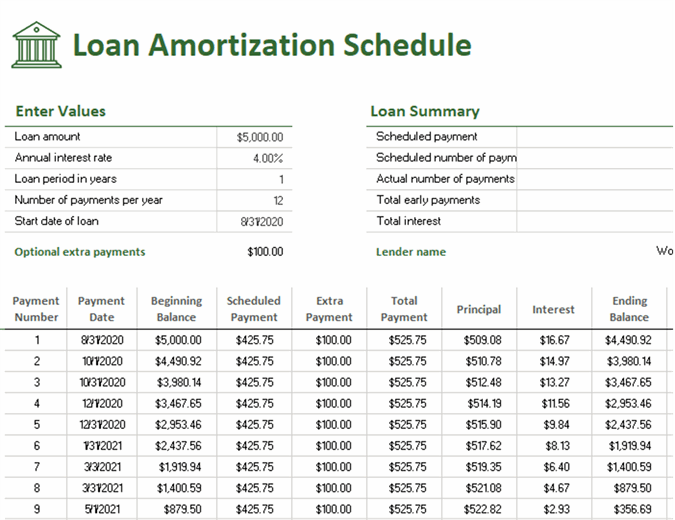
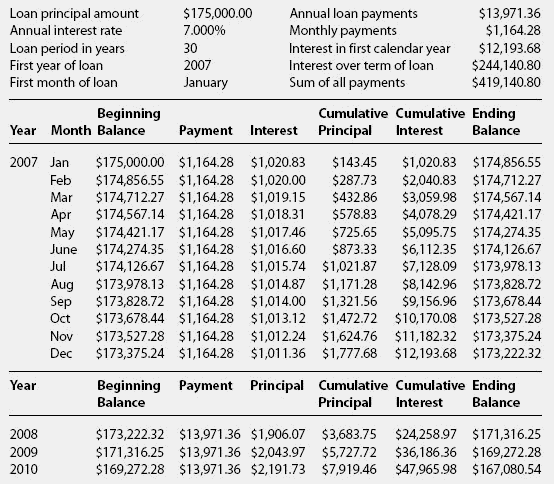
If the frequency or amount of your mortgage payments changes, then your amortization period will also change. The amortization period is based on a set number of regular and constant mortgage payments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
